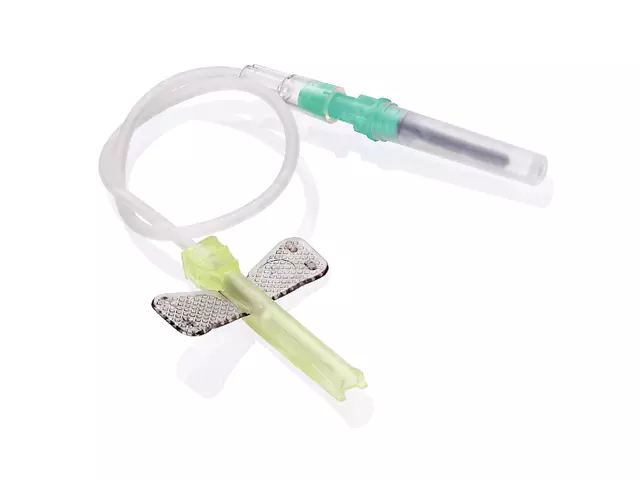
Non Vacuum Tubes: A Flexible and Diverse Blood Collection Tool
In modern medicine, blood collection is one of the most common and fundamental diagnostic methods. To ensure that the collected blood samples are accurate and meet various testing needs, the medical field employs a variety of blood collection equipment. Among them, non vacuum tubes are widely used in clinical practice due to their unique design and applications. In this article, kangjian will introduce the structural characteristics and clinical applications of non vacuum tubes in detail.
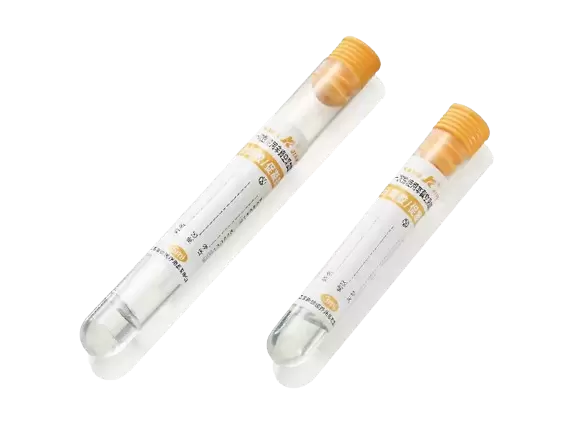

Structural Characteristics of Non Vacuum Tubes
Although the design of non vacuum tubes is relatively simple, their performance and effectiveness in clinical use largely depend on the various components of their structure. The design of every detail directly affects the efficiency of blood collection, sample quality, and the accuracy of test results.
1. Blood Collection Tube Body
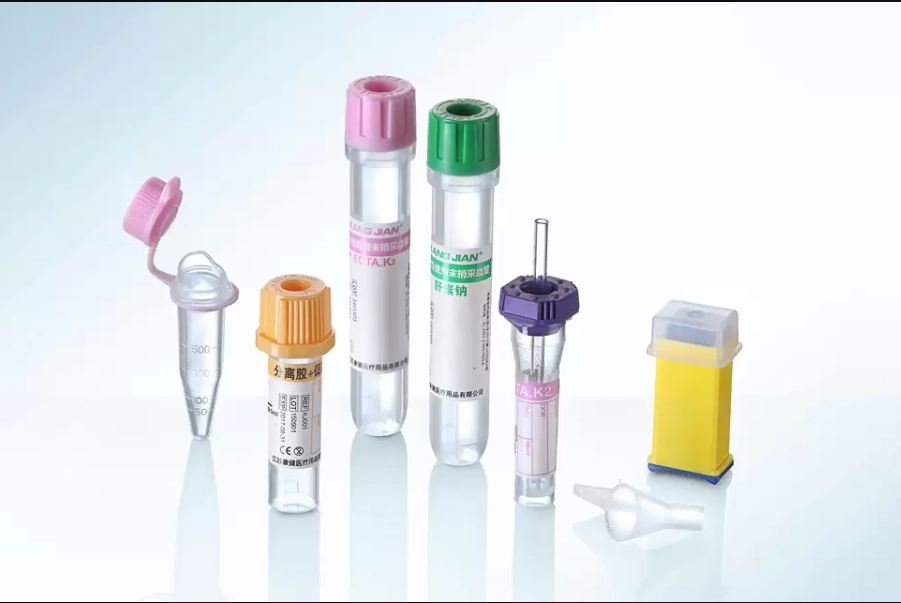
The main structure of non vacuum tubes is usually made of high-strength plastic or glass to ensure sufficient rigidity and pressure resistance during blood collection. Glass blood collection tubes are typically used in precise blood tests because glass can better prevent blood sample contamination or chemical reactions. Plastic blood collection tubes are more commonly used in general clinical blood collection due to their lower cost and safety. The volume of a blood collection tube generally ranges from 1 to 5 ml, depending on the amount of blood required for the test. The tube body is usually transparent, allowing medical staff to easily observe whether the collected blood volume meets the required amount. Additionally, the scale on the tube body helps medical staff accurately control the collection volume.
2. Sealing Cap
The sealing cap of the non vacuum tube not only provides protection but also effectively prevents blood leakage and external contaminants from entering the tube. After the blood collection is completed, medical staff can quickly seal the tube to ensure that the blood sample remains stable during subsequent processing and transportation. The design of the sealing cap usually incorporates multiple color codings to differentiate between tubes for various purposes. For instance, a purple sealing cap typically indicates that the blood collection tube is used for anticoagulant blood testing, while a red sealing cap is used for serum analysis. This color-coding system enables medical staff to quickly identify the type of blood collection tube, reducing the risk of errors.
3. Additives
Depending on the requirements of different test items, non vacuum tubes may contain specific chemical additives to process blood samples, making them suitable for various types of tests. Common additives include anticoagulants, coagulants, and separation gels.
Anticoagulants: Such as EDTA and heparin, are used to prevent blood from clotting in the collection tube, suitable for blood routine tests, blood gas analysis, and other tests.
Coagulants: These are used to accelerate blood coagulation and separate serum from blood cells, making them suitable for serological tests.
Separation Gel: This helps serum and blood cells separate quickly during centrifugation, providing purer serum samples, suitable for tests that require high-purity serum.
Each additive serves a specific purpose, and the blood collection tube is prepared with the appropriate additive during production to ensure the stability and accuracy of the blood sample during testing.
Clinical Applications of Non Vacuum Tubes
Non vacuum tubes are widely used in various clinical settings, especially in special situations where their flexibility and operability make them particularly useful. They play an irreplaceable role in cases where precise control over the amount of blood collected is essential.
1. Venous Blood Collection
Non vacuum tubes are often used for venous blood collection, especially for specific patient groups, such as children, the elderly, and patients with fragile blood vessels. These patients may have thin vascular walls or slow blood flow, and using vacuum blood collection tubes could cause discomfort or collapse of the vein. In such cases, the manual control advantage of non vacuum tubes can be fully utilized. Medical staff can gradually guide blood into the collection tube by adjusting the blood collection speed, thereby reducing discomfort for the patient. Additionally, non vacuum tubes perform well in cases where only a small amount of blood is required, such as microbiological analyses or micro-assays. Their use can effectively avoid unnecessary blood waste.
2. Small Laboratory Testing
Non vacuum tubes are widely used in small laboratories, especially when fast and accurate blood sample collection is required. Due to their ability to flexibly control the amount of blood collected, non vacuum tubes have obvious advantages in tests that require only a small amount of blood. For example, in certain enzymatic tests, biochemical analyses, or micro-serum tests, only 1-2 ml of blood is needed to complete the experiment. Non vacuum tubes can accurately collect the required amount of blood without wasting excess samples. Additionally, small laboratories often handle small sample volumes, and the cost-effectiveness and ease of operation of non vacuum tubes make them an ideal choice in these settings.
3. Blood Gas Analysis
Non vacuum tubes are widely used in arterial blood gas analysis. Blood gas analysis requires precise blood samples collected from the patient's artery to measure parameters such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and acid-base balance. Non vacuum tubes allow medical staff to better control the amount of blood collected and prevent the collection of excessive blood. At the same time, manual blood collection reduces the risk of air entering the sample, ensuring the accuracy of blood gas analysis results. Arterial blood gas analysis typically requires fast and precise blood sample handling, and the flexible design of non vacuum tubes meets these needs.
4. Slow Blood Collection Requirements
Some patients with specific conditions, such as coagulation disorders or elderly individuals, often require a slower blood collection speed. When using vacuum blood collection tubes, the rapid suction of blood may cause adverse reactions in these patients, potentially leading to vascular damage or bleeding. The manual operation of non vacuum tubes allows for controlled blood collection, reducing pressure on blood vessels, minimizing the risk of bleeding, and ensuring the safety of the blood collection process. Situations requiring slow blood collection include hemodialysis, routine blood monitoring in chemotherapy patients, and blood testing in patients with abnormal coagulation functions. Using non vacuum tubes helps medical staff better protect patients' blood vessels during collection, reducing adverse reactions.
Non vacuum tubes play an important role in the medical field due to their unique structural characteristics and wide range of clinical applications. They offer flexibility and precision in blood collection and have proven irreplaceable advantages in routine clinical testing, special patient populations, and specific diagnostic procedures. As medical technology continues to advance, non vacuum tubes will remain an essential tool for healthcare professionals, providing more effective support for medical diagnoses and treatments while promoting the development of the medical industry.